How to Create a Timeseries in Python
07.05.2021
Intro
Time series is one of the most common analysis and modeling in Data Science. In this article, we will learn how to create time series in python.
Creating a Basic Time Series
To create a time series in Python, we use a normal DataFrame from python. However, we make one small change, which is we index the data by the date column. Let's see an example.
import pandas as pdLet's say we have a list of sales numbers and a list of dates for those sales as below. We begin by creating a data frame from this data.
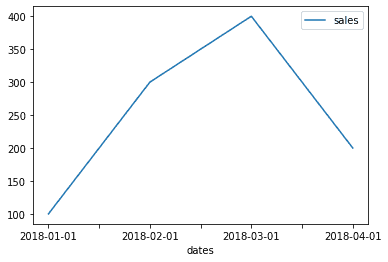
sales = [100, 300, 400, 200]
dates = ['2018-01-01', '2018-02-01', '2018-03-01', '2018-04-01']df = pd.DataFrame.from_dict({
'dates': dates,
'sales': sales
})
df.head()| dates | sales | |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 2018-01-01 | 100 |
| 1 | 2018-02-01 | 300 |
| 2 | 2018-03-01 | 400 |
| 3 | 2018-04-01 | 200 |
Next, we convert our data column to python datetimes using the to_datetime method from pandas. Then, we use the set_index method from the DataFrame to change our date from index by 0-N to our dates.
df['dates'] = pd.to_datetime(df['dates'])
df.set_index('dates')| sales | |
|---|---|
| dates | |
| 2018-01-01 | 100 |
| 2018-02-01 | 300 |
| 2018-03-01 | 400 |
| 2018-04-01 | 200 |
And that's it! Now pandas will tree our data set like a time series.
df.plot(x = "dates", y = "sales")<AxesSubplot:xlabel='dates'>