How to Create a ggplot Line Plot in R
06.01.2021
Intro
Line plots are used to show a continous varaible compared to an ordinal varaible. Most commonly line plots are used to show how some varaible changes over time. In this article, we will learn how to create ggplot line plots in R.
If you are in a rush
For those with little time, here is a quick snippet of Line plots. Read on for more details.
library(tidyverse)## -- Attaching packages --------------------------------------- tidyverse 1.3.1 --
## v ggplot2 3.3.3 v purrr 0.3.4
## v tibble 3.1.0 v dplyr 1.0.5
## v tidyr 1.1.3 v stringr 1.4.0
## v readr 1.4.0 v forcats 0.5.1
## -- Conflicts ------------------------------------------ tidyverse_conflicts() --
## x dplyr::filter() masks stats::filter()
## x dplyr::lag() masks stats::lag()data(economics)
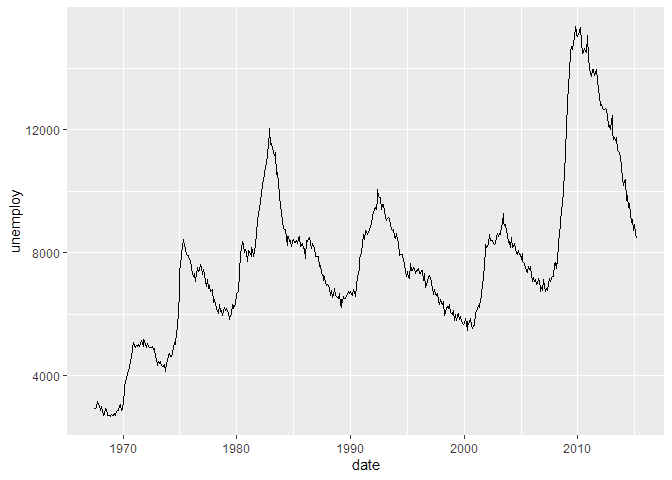
ggplot(economics, aes(x = date, y = unemploy)) +
geom_line()Loading the Data
For our tutorial, we will use the economics data set that comes with
the ggplot package.
library(tidyverse)
data(economics)
## Add year as a factor for later use
economics$year <- format(as.Date(economics$date, format="%d/%m/%Y"),"%Y")
glimpse(economics)## Rows: 574
## Columns: 7
## $ date <date> 1967-07-01, 1967-08-01, 1967-09-01, 1967-10-01, 1967-11-01, ~
## $ pce <dbl> 506.7, 509.8, 515.6, 512.2, 517.4, 525.1, 530.9, 533.6, 544.3~
## $ pop <dbl> 198712, 198911, 199113, 199311, 199498, 199657, 199808, 19992~
## $ psavert <dbl> 12.6, 12.6, 11.9, 12.9, 12.8, 11.8, 11.7, 12.3, 11.7, 12.3, 1~
## $ uempmed <dbl> 4.5, 4.7, 4.6, 4.9, 4.7, 4.8, 5.1, 4.5, 4.1, 4.6, 4.4, 4.4, 4~
## $ unemploy <dbl> 2944, 2945, 2958, 3143, 3066, 3018, 2878, 3001, 2877, 2709, 2~
## $ year <chr> "1967", "1967", "1967", "1967", "1967", "1967", "1968", "1968~Creating a Basic ggplot Line Plot
To create a Line plot in ggplot2, we can use the geom_line method
after supplying a continuous variable to the y of our aes, aesthetic.
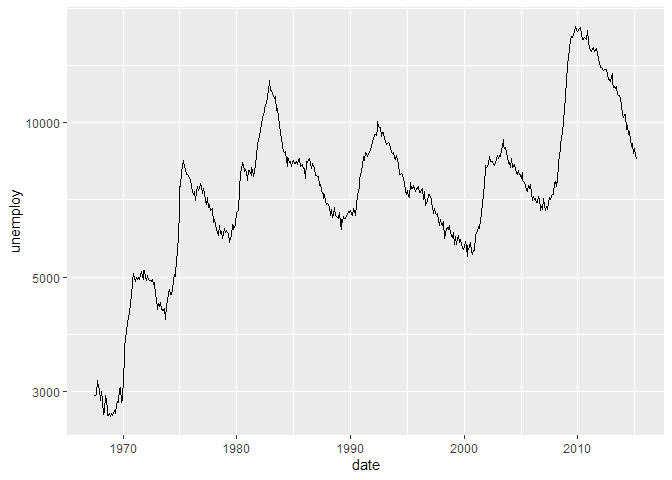
In this example, we will plot unemployment over time.
ggplot(economics, aes(x = date, y = unemploy)) +
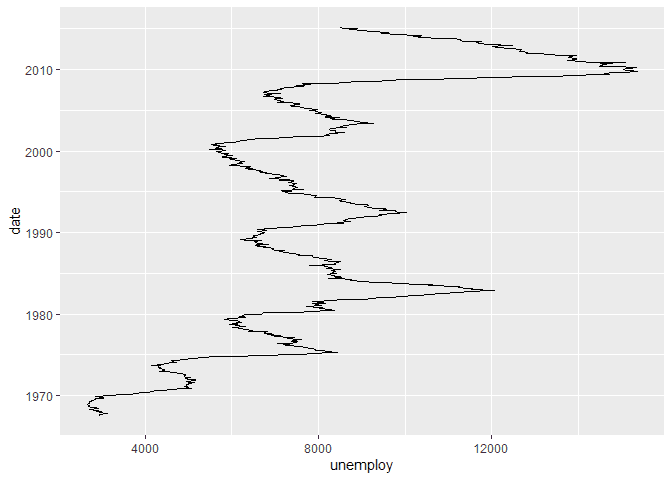
geom_line()We can also flip the plot to orient horizontally by using the
coord_flip method.
ggplot(economics, aes(x = date, y = unemploy)) +
geom_line() +
coord_flip()Customizing the ggplot Line Plot
We can customize our Line plots using some parameters on the geom_line
method. For example, we can change the color using the color named
parameter. Here is an example.
ggplot(economics, aes(x = date, y = unemploy)) +
geom_line(color = 4,
fill = 4,
alpha = 0.25)## Warning: Ignoring unknown parameters: fillAdjusting the ggplot Line Plot Labels
We can adjust the title, x-label, and y-label of our Line plot using the
labs method. We then pass the title, x and y parameters.
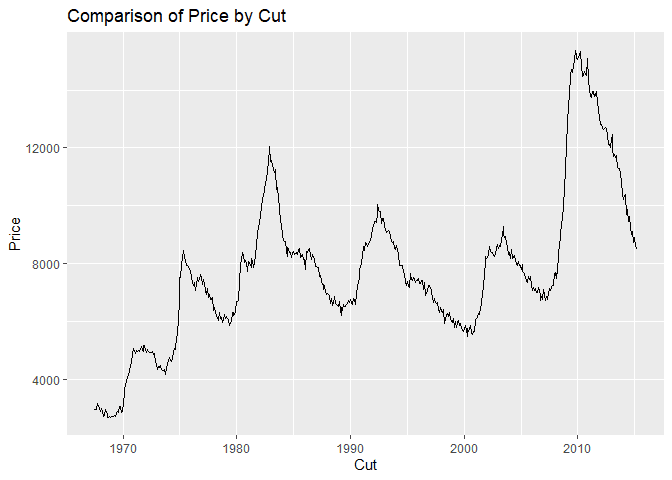
ggplot(economics, aes(x = date, y = unemploy)) +
geom_line() +
labs(
title = "Comparison of Price by Cut",
x = "Cut",
y = "Price"
)Group by Color
We can color the separate groups of our violin plots by using the fill
or colour aesthetic properties. Here is an example of using the
colour to assign colors to each factor.
library(ggplot2)
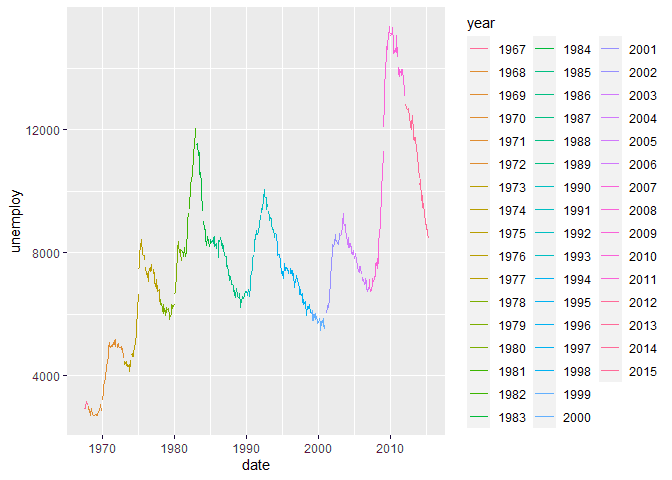
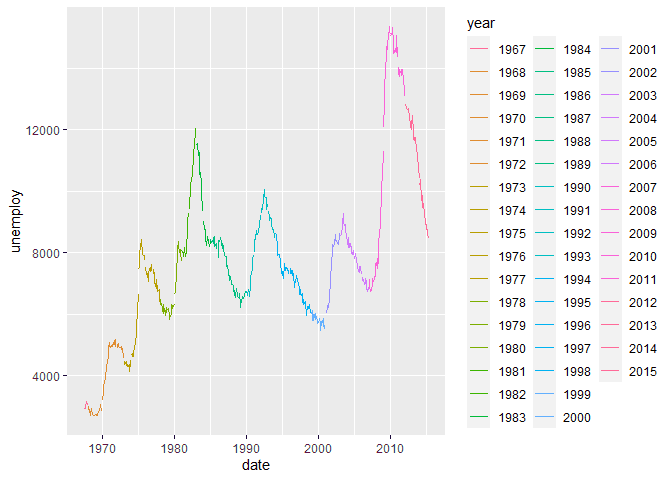
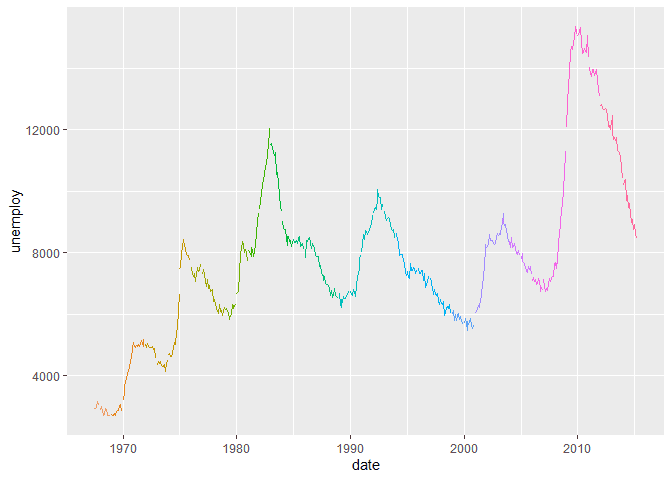
ggplot(economics, aes(x = date, y = unemploy, colour = year)) +
geom_line()Facets Groups on a ggplot Line Plot
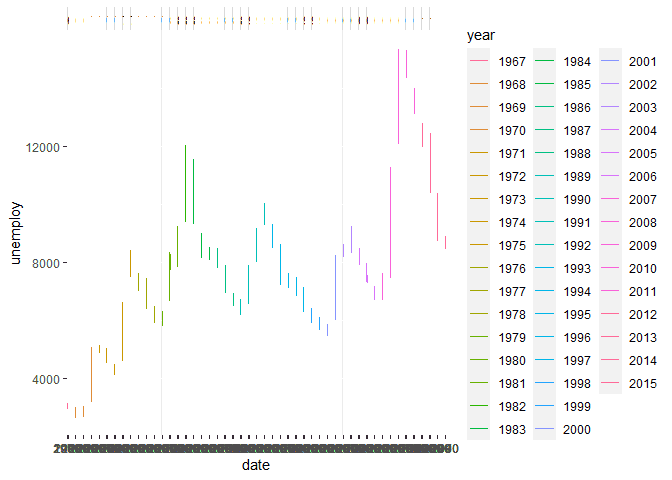
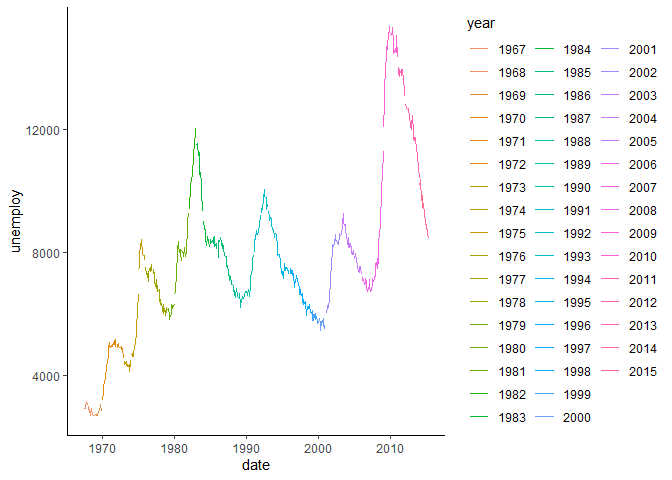
If we prefer to have separate plots, we can use the facet_ methods in
ggplot. For example, here are plots separated by each year.
library(ggplot2)
ggplot(economics, aes(x = date, y = unemploy, colour = year)) +
geom_line() +
facet_grid(~year)Limiting X and Y
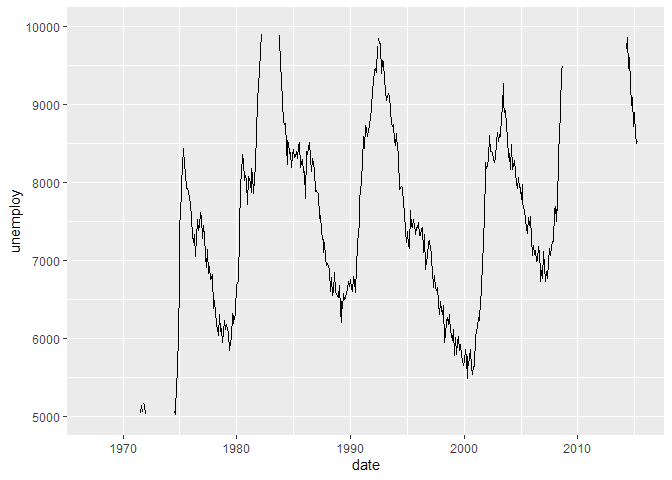
If we would like to limit the y values of our plots, we can use the
ylimit function
ggplot(economics, aes(x = date, y = unemploy)) +
geom_line() +
ylim(5000, 10000)## Warning: Removed 41 row(s) containing missing values (geom_path).Scaling X and Y
We can also scale the y axis using the scale_ function from ggplot.
Here are some example of a log10 and sqrt scale of the y axis.
ggplot(economics, aes(x = date, y = unemploy)) +
geom_line() +
scale_y_log10()ggplot(economics, aes(x = date, y = unemploy)) +
geom_line() +
scale_y_sqrt()Color and Fill Scales
There are many color options in ggplot. We can use scale_ methods like
scale_fill_brewer() to have ggplot automatically assign different
themes based on our data set.
library(ggplot2)
ggplot(economics, aes(x = date, y = unemploy, colour = year)) +
geom_line() +
scale_fill_brewer()Customizing the Legend of a ggplot Line Plot
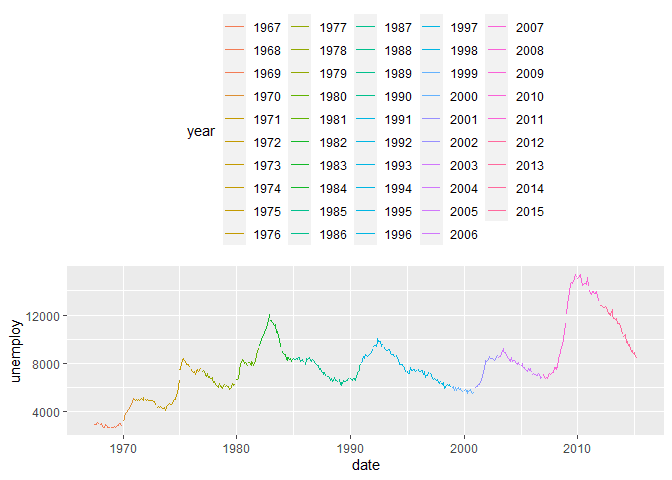
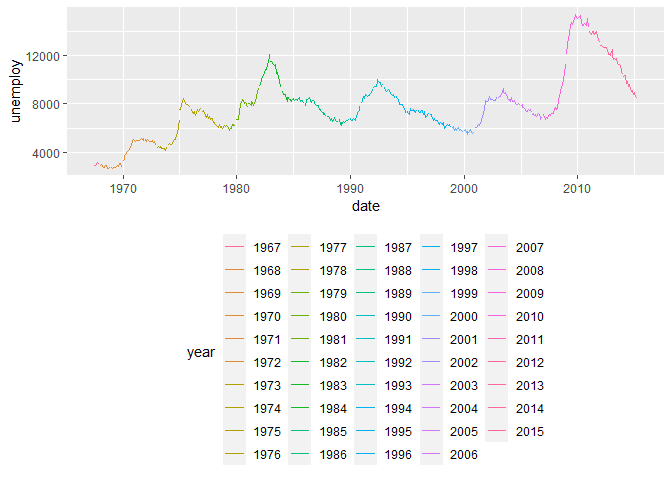
When we have groups, ggplot will add a legend to the plot. We can
customize the position of this legend using the theme method and the
legend.position parameter. Here are example of moving the legend to
the top, bottom, and hiding it.
ggplot(economics, aes(x = date, y = unemploy, colour = year)) +
geom_line() +
theme(legend.position="top")ggplot(economics, aes(x = date, y = unemploy, colour = year)) +
geom_line() +
theme(legend.position="bottom")ggplot(economics, aes(x = date, y = unemploy, colour = year)) +
geom_line() +
theme(legend.position="none")Using Themes with a ggplot Line Plot
If we want to use built in styles for the full plot, ggplot provides
themes to add to our plot. Here is an example of adding the
theme_classic to our plot.
ggplot(economics, aes(x = date, y = unemploy, colour = year)) +
geom_line() +
theme_classic()Adding Summary Information to a ggplot Line Plot
We can also add summary information to our Line plots to visualize in
addition to our distributions. For example, we can use the
stat_summary method to display the median like so.
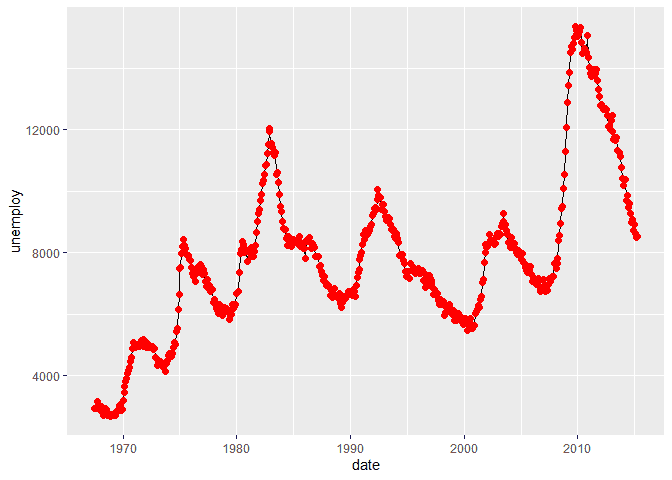
ggplot(economics, aes(x = date, y = unemploy)) +
geom_line() +
stat_summary(
fun.y = median,
geom = "point",
size = 2,
color = "red"
)## Warning: `fun.y` is deprecated. Use `fun` instead.Similarly, we can add the mean to each of our plots.
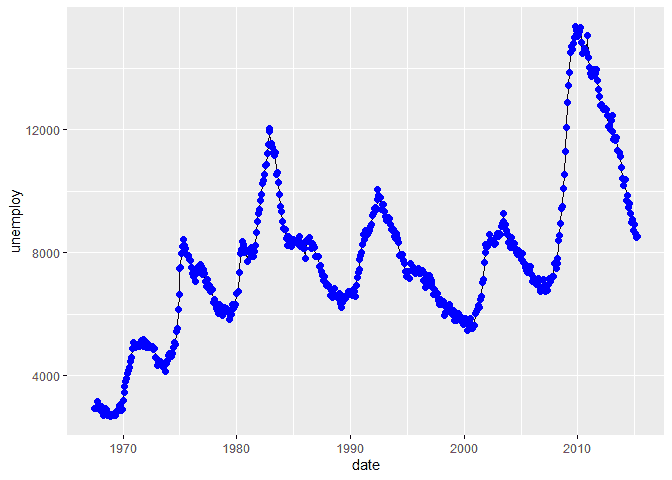
ggplot(economics, aes(x = date, y = unemploy)) +
geom_line() +
stat_summary(
fun.y = mean,
geom = "point",
size = 2,
color = "blue"
)## Warning: `fun.y` is deprecated. Use `fun` instead.